Fetch()API及相关基础
fetch API基础
一 · 基本用法
fetch()是 XMLHttpRequest 的升级版,用于在 JavaScript 脚本里面发出 HTTP 请求
fetch('url')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
在用法上,fetch()接受一个 URL 字符串作为参数,默认向该网址发出 GET 请求,返回一个 Promise 对象,支持.then的链式写法
二 · Response对象
fetch()请求成功以后,得到的是一个 Response对象。它对应服务器的 HTTP 回应。
Response对象根据服务器返回的不同类型的数据,提供了不同的读取方法。
response.text():得到文本字符串。response.json():得到 JSON 对象。response.blob():得到二进制 Blob 对象。response.formData():得到 FormData 表单对象。response.arrayBuffer():得到二进制 ArrayBuffer 对象。
fetch('https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2020/12/fetch-tutorial.html')
.then(response => response.text())
.then(data => console.log(data))
三 · fetch的第二个参数
fetch()的第一个参数是 URL,还可以接受第二个参数,作为配置对象,定制发出的 HTTP 请求。
fetch()第二个参数的完整 API 如下。
const response = fetch(url, {
method: "GET", //http请求方法
headers: { //定制http请求的标头
"Content-Type": "text/plain;charset=UTF-8"
},
body: undefined, //post请求的数据体
referrer: "about:client",
referrerPolicy: "no-referrer-when-downgrade",
mode: "cors",
credentials: "same-origin",
cache: "default",
redirect: "follow",
integrity: "",
keepalive: false,
signal: undefined
});
四 · async和await
async和await关键字让我们可以用一种更简洁的方式写出基于Promise的异步行为,而无需刻意地链式调用Promise
async函数的返回值是一个promise
使用async/await的目的为了简化使用基于promise的API时所需的语法。
4.1 async
async函数一定会返回一个promise对象。如果一个async函数的返回值看起来不是promise,那么它将会被隐式地包装在一个promise中。
例如,如下代码:
async function foo() {
return 1
}
等价于:
function foo() {
return Promise.resolve(1)
}
4.2 await
await只在async函数内有效,如果你在async函数体之外使用它,就会抛出语法错误
let e = await 78910;
console.log(e);
当promise的状态为resolve时,await返回其result的值
async function myFun () {
let str = Promise.resolve('hello world')
console.log(str)
let p = await str
console.log(p)
//let str = await Promise.resolve('hello world')
}
当promise的状态为reject时,则需要通过try/catch来获取result
async function myFun () {
let str = Promise.reject('byebye world')
console.log(str)
try {
let p = await str
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
}
}
五 · 案例分享
fetch("http://jwxt.neuq.edu.cn/eams/courseTableForStd!courseTable.action", {
"headers": {
"accept": "*/*",
"accept-language": "zh-CN,zh;q=0.9",
"content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"x-requested-with": "XMLHttpRequest"
},
"referrer": "http://jwxt.neuq.edu.cn/eams/courseTableForStd.action",
"referrerPolicy": "strict-origin-when-cross-origin",
"body": "ignoreHead=1&showPrintAndExport=1&setting.kind=std&startWeek=&semester.id=50&ids=15187",
"method": "POST",
"mode": "cors",
"credentials": "include"
});
六 · fetch和axios的对比
6.1 兼容性
Axios可以兼容IE浏览器,而Fetch在IE浏览器和一些老版本浏览器上没有受到支持,但是有一个库whatwg-fetch,可以让老版本浏览器支持Fetch ,但是现在很多网站的开发都为了减少成本而选择不再兼容IE浏览器。
各个浏览器对Fetch的兼容:
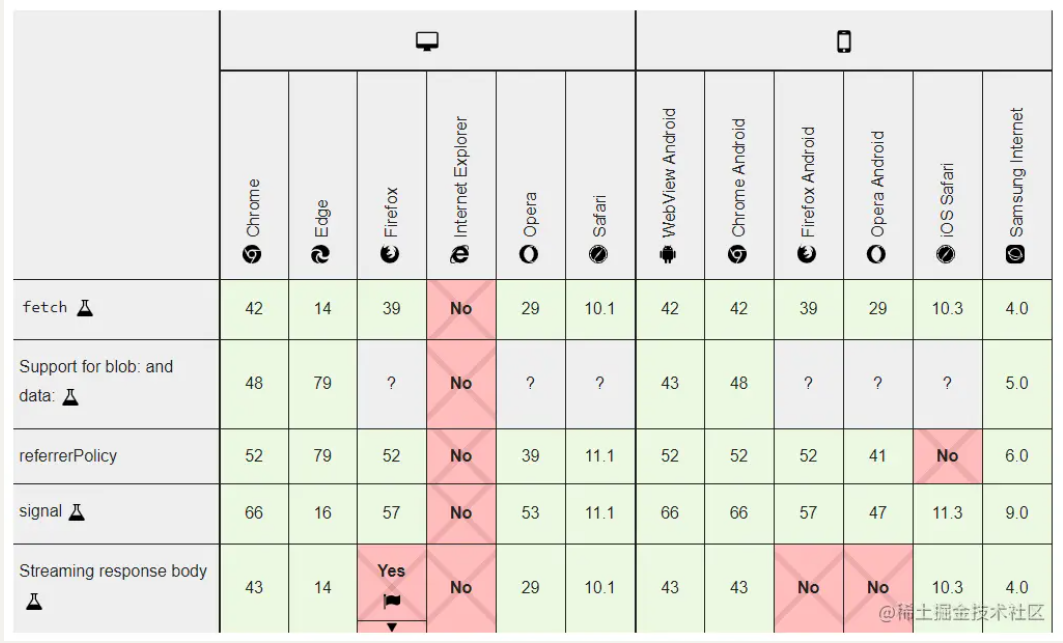
6.2 请求方式
axios:
const options = {
url: "url",
method: "POST",
headers: {
Accept: "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json;charset=UTF-8",
},
data: {
a: 10,
b: 20,
},
};
axios(options).then((response) => {
console.log(response.status);
});
fetch:
const options = {
method: "POST",
headers: {
Accept: "application/json",
"Content-Type": "application/json;charset=UTF-8",
},
body: JSON.stringify({
a: 10,
b: 20,
}),
};
fetch('url', options).then((response) => {
console.log(response.status);
});
其中最大的不同之处在于传递数据的方式不同,axios是放到data属性里,以对象的方式进行传递,而fetch则是需要放在body属性中,以字符串的方式进行传递。
6.3 数据转化
axios还有非常好的一点就是会自动对数据进行转化,而fetch则不同,它需要使用者进行手动转化。
// axios
axios.get("url").then(
(response) => {
console.log(response.data);
},
(error) => {
console.log(error);
}
);
// fetch
fetch("url")
.then((response) => response.json()) // 需要对响应数据进行转换
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
})
.catch((error) => console.error(error));
这就需要我们清楚请求后的数据类型是什么,再选择合适的方法进行转化
6.4 浏览器原生支持
fetch()是es6之后一个原生的API,是 XMLHttpRequest 的升级版,所以它天生有一项优势就是现代浏览器的原生支持。打开浏览器控制台使用fetch不需要什么配置就可以直接进行请求。
在很多文章中可以看到作者的评价,说浏览器原生支持几乎是fetch对axios唯一的优势。
七 · 最后
拿fetch和axios相比较似乎不太公平,因为axios是对XMLHttpRequest 的封装,而fetch仅仅是一个新兴的API。
fetch理论上可以实现axios能够实现的所有功能,但是需要自行进行封装。在项目中,axios应该仍然是最好的选择。
但有时候新技术取代老技术是一个必然趋势,所以fetch有一天终将会取代XMLHttpRequest,也许之后axios库会改为使用fetch请求。
内容参考: